About
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) in Andhra Pradesh
MIDH is a centrally sponsored scheme launched by the Government of India under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare. The primary aim of MIDH is to promote the holistic growth and development of the horticulture sector, which includes fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic & plantation plants.
Objectives of MIDH
Enhance Horticulture Production: To increase the production of horticultural crops through area expansion, productivity enhancement, and improved post-harvest management.
Promote Integrated Development: To ensure the comprehensive development of the horticulture sector, focusing on forward and backward linkages.
Improve Infrastructure: To develop and enhance the infrastructure for storage, marketing, and processing of horticultural produce.
Research and Development: To support research, technology development, and dissemination to farmers for the improvement of horticultural practices.
Capacity Building: To provide training and capacity building to farmers, extension workers, and other stakeholders involved in horticulture.
Organic Farming: To promote organic farming and good agricultural practices in horticulture.
Key Components
Area Expansion and Production: This includes activities like the introduction of high-yielding varieties, establishment of nurseries, and plantation of horticultural crops. Rejuvenation of Old Orchards: Rejuvenating old and unproductive orchards to improve productivity. Protected Cultivation: Promotion of greenhouse and shade net cultivation for high-value horticultural crops. Post-Harvest Management: Development of post-harvest infrastructure like pack houses, cold storages, and ripening chambers. Marketing and Processing: Establishment of market infrastructure and promotion of value addition through processing units. Creation of Water Resources: Efficient water management practices including drip and sprinkler irrigation systems.
Funding Pattern
Central and State Share: The funding pattern typically involves a central 60% and state government 40% share Beneficiary Contribution: In certain components, there is also a beneficiary contribution to ensure ownership and involvement of the farmers.
Achievements and Impact
Increased Horticultural Production: Significant increase in the area under horticultural crops and productivity improvements. Infrastructure Development: Enhanced post-harvest infrastructure and marketing facilities have reduced wastage and improved market access for farmers. Enhanced Farmer Income: Quality production and Higher productivity are better market linkages have led to increased income for farmers engaged in horticulture. Technology Adoption: Increased adoption of modern horticultural practices and technologies by farmers.
Challenges and Future Directions
Climate Resilience: Addressing the challenges posed by climate change and ensuring the resilience of horticultural crops. Market Access: Further improving market access and ensuring fair prices for farmers. Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable, organic and integrated crop management practices. Capacity Building: Continued focus on capacity building and training for farmers and extension workers.
Overall, MIDH in Andhra Pradesh plays a crucial role in enhancing the horticulture sector's growth and development, contributing significantly to the state's agricultural economy and farmers' livelihoods.
Area Of Operation
1. Srikakulam 15.Y.S.R Kadapa
2. Parvathipuram Manyam 16.Nandyal
3. Anakapalli 17.Kurnool
4. Alluri Seetharamaraju 18.Ananthapur
5. West Godavari 19.Sri Satya Sai
6. Eluru 20.Chittoor
7. NTR 21.Yanadis(Nellore)
8. Guntur 22. ITDA Rampachodavaram
9.Palnadu 23.ITDA Paderu
10.Bapatla 24.ITDA, Parvathipuram
11.Prakasam 25.ITDA Seethampeta
12.SPSR Nellore 26.ITDA Chintoor
13.Tirupati 27. ITDA K.R. Puram
14.Annamayya 28.ITDA Chenchu(Srisailam)

Annual Action Plan 2025-26
An annual plan is crucial as it sets a roadmap for achieving long-term goals, providing clarity and direction. It helps prioritize tasks, allocate resources effectively, and measure progress over time. By outlining objectives and strategies, it enhances coordination among team members and fosters accountability. Ultimately, a well-crafted annual plan promotes organizational alignment and adaptability to changing circumstances.
- ■ Total AAP 2025-26 : Rs. 218.75 Crore
- ■ GoI Share: Rs. 131.25 Crore
- ■ State Share: Rs. 87.50 Crore
- ■ ACTION PLAN 2025-26-MIDH
Achievements from 2014-15 to 2024-25
| Serial No. | Component | Achievement |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Area Brought under Fruits, Flowers and vegetable cultivation | 1,36,041 Ha |
| 2 | Rejuvenation of Mango & Cashew | 33,421 Ha |
| 3 | Farm ponds | 3519 Nos |
| 4 | Cold Storages assisted | 117 Nos |
| 5 | Ripening chambers established | 78 Nos |
| 6 | Area Covered under Mulching | 44,396 Ha |
| 7 | Area Covered under Poly Houses | 127 Ha |
| 8 | Area brought under Shadenet Houses | 371 Ha |

Annual Action Plan 2025-26
The food demand is increasing day-by-day due to burgeoning population of the country. In order to make pace with food demand and over increasing population, there is an urgent need to enhance the productivity of crops. Sometimes, climatic variation and other natural adversities such as flood, drought, cyclone, hail and storm etc. cause poor crop production or total crop failures. So, there is an urgent need of appropriate technology in the field of agriculture to meet out the food demand of rapidly increasing population. Therefore, it is need of the hour to bridge the gap in between food demand and increasing population.
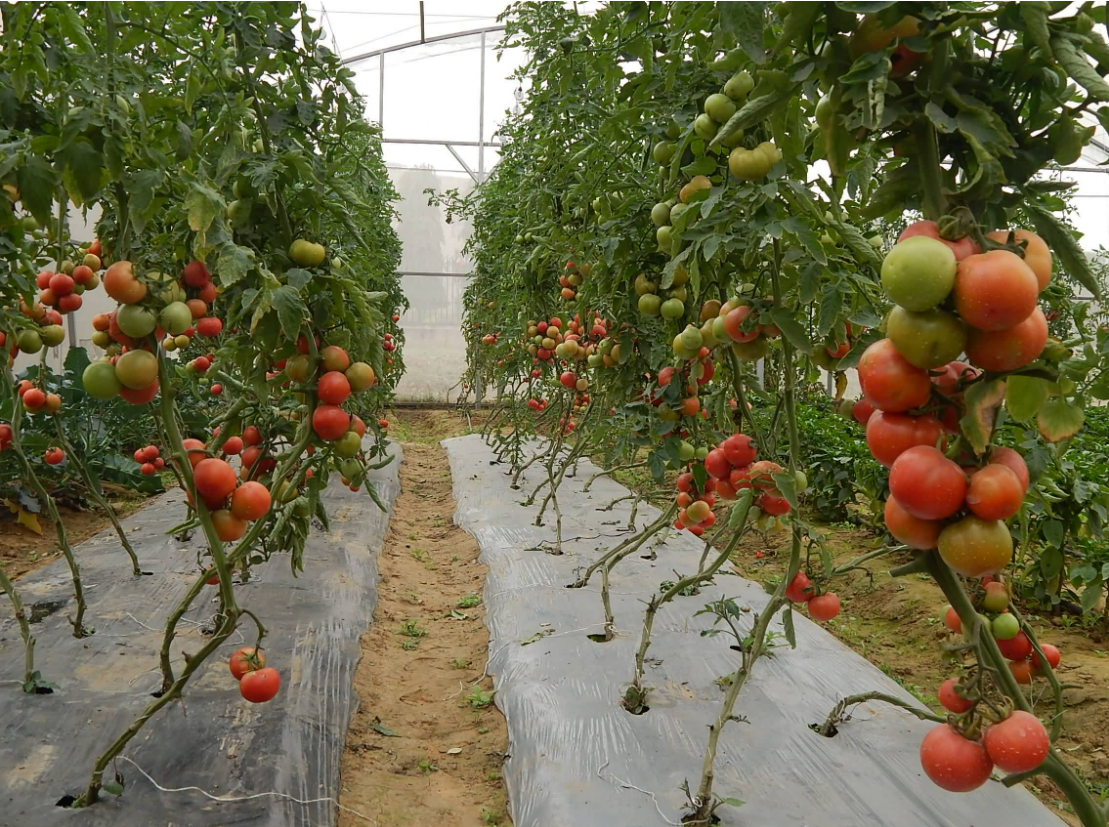
Protected cultivation is one of the leading technologies to meet the requirement of food especially there in horticulture sector. Production of crops under protected conditions has great potential in augmenting production and quality of vegetables, flowers and some fruit crops in main and off season and maximising water and nutrients use efficiency under varied agro-climatic conditions of the country. At present in our country, the area under protected cultivation is around 25,000 ha. While the area under protected cultivation of vegetables is about 2000 ha. Leading States in protected cultivation in India are Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Haryana, J & K, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
The major crops that are grown under Polyhouse are Capsicum, English Cucumber, Hybrid Tomato, Gerbera, Carnation and Roses.
As on today, the following crops are grown in Polyhouses / Shadenet Houses. The average production and net value are as follows:
| SI No. | Crop | Unit Size (Sq.Mtrs.) | Production (Tons) | Avg. Rate per Kg(Rs.) | Avg. Gross Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Capsicum | 4000 | 50 – 60 | 30 | Rs.15.00 lakhs per 4000 Sq.mtrs. |
| 2 | English Cucumber | 4000 | 20 – 30 | 10 | Rs.2.00 – 3.00 lakhs per 4000 Sq.mtrs. |
| 3 | Hybrid Tomato | 4000 | 75 | 10 | Rs.7.00 – 8.00 lakhs per 4000 Sq.mtrs. |
| 4 | Nursery | 4000 | 7 lakhs Seedlings per cycle – Total 21.00 lakhs for 3 cycles | 0.5 - 0.75 | 15.75 lakhs |
The total area covered under Protected Cultivation is 284.07 Ha. (i.e., 710.18 Acres / 28.40 lakh Sq. Mtrs.). The approximate gross returns out of 710.18 Ac. Is Rs.71.01 crores (@ Rs.10.00 lakhs gross value for 4000 sq.mtr. or 1 Ac.).
| S. No. | Name of the District | Polyhouse (Area in Ha.) | Shadenet House (Area in Ha.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SRIKAKULAM | 2.31 | 0.20 |
| 2 | VIZIANAGARAM | 4.29 | 5.28 |
| 3 | VISAKHAPATNAM | 1.2 | 3.14 |
| 4 | EAST GODAVARI | 20.37 | 2.76 |
| 5 | WEST GODAVARI | 6.71 | 3.98 |
| 6 | KRISHNA | 7.15 | 19.81 |
| 7 | GUNTUR | 1.52 | 111.61 |
| 8 | PALNADU | 0.0 | 15.27 |
| 9 | BAPATLA | 0.40 | 3.00 |
| 10 | PRAKASAM | 0.69 | 91.05 |
| 11 | SPSR NELLORE | 2.02 | 7.20 |
| 12 | TIRUPATI | 2.32 | 1.00 |
| 13 | CHITTOOR | 29.59 | 11.43 |
| 14 | ANNAMAYYA | 0.40 | 0.00 |
| 15 | YSR KADAPA | 1.31 | 8.79 |
| 16 | KURNOOL | 7.82 | 19.96 |
| 17 | NANDYALA | 0.59 | 0.00 |
| 18 | ANANTHAPURAM | 34.00 | 12.75 |
| TOTAL | 122.69 | 317.23 | |
POST-HARVEST MANAGEMENT INFRASTRUCTURE AVAILABLE IN A.P
| Cold Storage Units | Ripening Chamber | Fruit Processing Units | Cashew Processing Units | Onion Storage Structures | Pack Houses | Integrated Pack House | Cold Rooms(30 MT) | Pre-cooling Units | Alternate Energy-Solar Power Grid Units | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (MTs) | No | Capacity (kWP) |
| 373 | 2060490 | 247 | 54316 | 174 | 66850 | 416 | 46170 | 122 | 3050 | 4762 | 142860 | 16 | 234 | 22 | 660 | 12 | 218 | 4 | 355.5 |
REQUIREMENT OF PHM UNITS AS PER NCCD SURVEY
| Sl. No | Name of the Unit | No. | Capacity (MTs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cold Storage | 72 | 451492 |
| 2 | Ripening Chambers | 128 | 38520 |
| 3 | Cashew Processing Units | 32 | 4800 |
| 4 | Integrated Pack House | 58 | 3480 |
| 5 | Refrigerated Vans | 48 | 432 |
| 6 | Functional Pack House | 3124 | 6248 |
| 7 | Onion Storage Structures | 22051 | 551273 |

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)